The Axial Seamount, an undersea volcano located approximately 470 kilometers off the coast of Oregon, is exhibiting signs of increased volcanic activity.
Scientists believe an eruption could occur as early as 2025, based on observations of ground deformation, rising seismic activity, and magma accumulation. This prediction is a significant breakthrough in volcanic monitoring, as accurately forecasting eruptions remains a complex scientific challenge.
Axial Seamount: Advanced Monitoring and Key Observations
Axial Seamount, one of the world’s most closely studied underwater volcanoes, has been the subject of ongoing research. Real-time monitoring systems on the ocean floor continuously track its behavior, providing crucial insights.
A recent study, titled Axial Seamount Has Suddenly Woken Up! An Update on the Latest Inflation and Seismic Data and a New Eruption Forecast, was presented at the American Geophysical Union meeting. The study revealed critical indicators of a potential eruption:
- Surface Swelling: Similar ground deformation patterns were observed before the volcano’s last eruption in 2015.
- Earthquake Swarms: Increased seismic activity near the volcano indicates magma movement beneath the surface.
These patterns strongly resemble those preceding the 2015 eruption, reinforcing scientists’ belief that another eruption is imminent.
Advances in Volcanic Prediction Technologies
The potential eruption of Axial Seamount has spurred the development of cutting-edge predictive tools. Researchers are leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze seismic data recorded during the 2015 eruption. AI algorithms have identified specific patterns associated with magma migration, which could improve eruption forecasting accuracy.
Axial Seamount serves as a valuable testbed for these innovative technologies. If successful, these advancements could be applied to monitor and predict activity in other volcanic systems worldwide.
Implications and Global Relevance
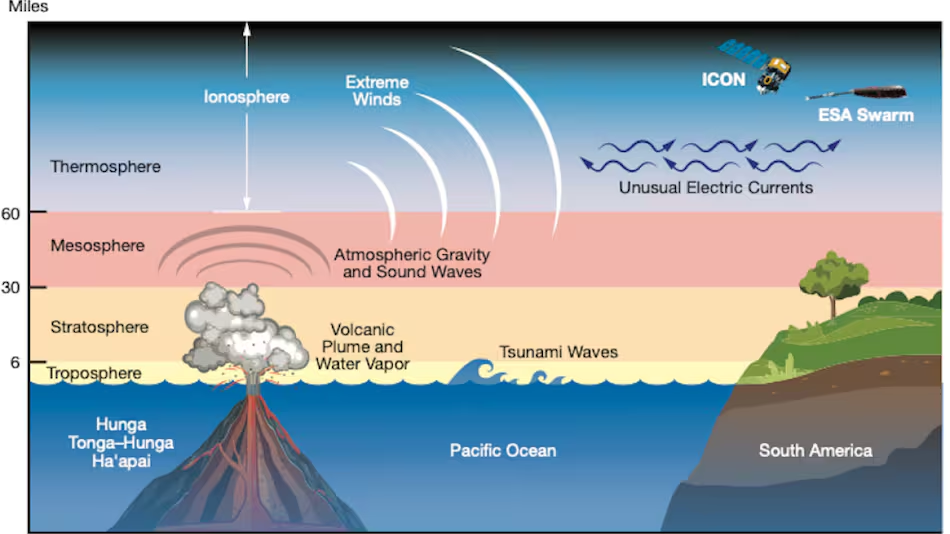
While Axial Seamount itself poses minimal immediate risk to human populations due to its remote location, the broader implications of an underwater eruption cannot be overlooked. The 2022 Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption, for example, triggered a Pacific-wide tsunami, underscoring the importance of preparedness and accurate forecasting.
Enhanced monitoring and early warning systems for Axial Seamount could provide critical lead time for coastal communities in the Pacific Northwest. Furthermore, the insights gained from this eruption could deepen our understanding of submarine volcanism and its potential global impacts.
Looking Ahead
As the predicted 2025 eruption approaches, scientists will continue to monitor Axial Seamount with advanced instruments and predictive models. These efforts aim to refine forecasting methods and improve our ability to anticipate volcanic events. The findings from this research have the potential to revolutionize volcanic monitoring systems and benefit communities far beyond the Pacific region.
Discover unbeatable daily deals from Amazon, now at Ampixi.com! 🛍️ Shop smart, save big! 💸✨
